Figure 1
Download original image
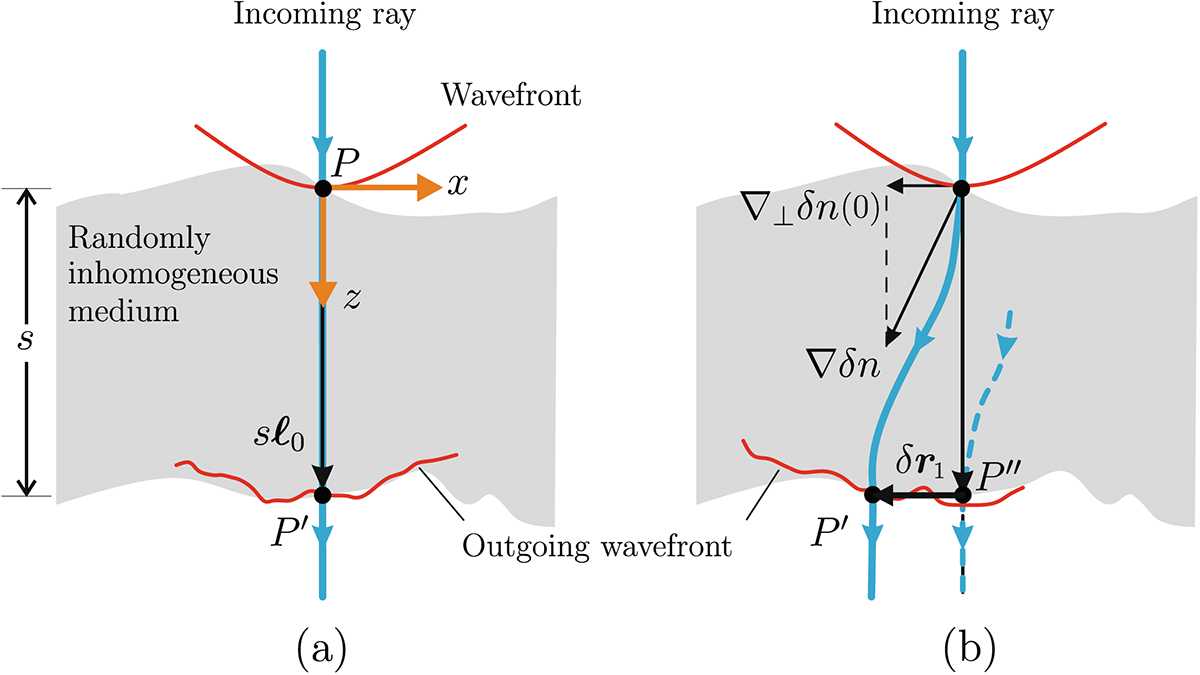
Scheme of typical effects experienced by the electromagnetic wave propagating through a slab of randomly inhomogeneous medium of thickness s. The conventional phase screen approach simulates the random corrugation of the incoming wavefront (a). The phase derivative screen adds the random refraction of the incoming signal ray (b). In the case of a sufficiently strong refractive index gradient ∇δn, the ray bends within the layer and appears to be displaced at distance δr1 from the original direction of propagation ℓ0. The dashed vector shows that, in contrast to case (a), a different ray emerges in the initial direction of ray propagation. The fluctuating part of the gained phase along the initial direction is then given by equation (14).
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.


